Whereas trade-offs are inevitable, consultants interviewed by crypto.information imagine the blockchain trilemma sheds mild on the challenges builders face and methods to take care of them.
Coined by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin in 2017, the blockchain trilemma highlights the challenges builders face when creating distributed ledger programs. In accordance with Buterin, architects should make trade-offs and prioritize two of the three key options.
In an interview with crypto.information, Luke Nolan, a analysis fellow at CoinShares, agreed with this view. Nolan believes that the blockchain trilemma in a broad sense successfully illustrates the problem of totally realizing all three traits. He emphasised that builders typically sacrifice some or each facets when optimizing one function.
The blockchain trilemma
Alex Dulub, founding father of Web3 Antivirus, means that dashing up a blockchain can generally compromise its safety. He believes that options akin to Layer-2 (L2) networks and sidechains, which deal with transactions exterior the principle blockchain, can improve velocity and scalability, however can even introduce new dangers.
Dulub thinks that bugs in sensible contracts, centralization dangers and potential assaults are the principle vulnerabilities for blockchains that need to enhance all three facets.
Neville Grech, the founding father of Dedaub, a blockchain safety firm, factors out that rising parameters akin to block measurement and frequency to enhance velocity can require extra computing energy, bandwidth and storage than common nodes can deal with. This might result in a extra centralized community construction, with only some nodes totally collaborating within the blockchain.
Whereas adjusting the validation course of might velocity up a community, Grech warns that “it might expose the blockchain to vulnerabilities and create validation disputes and short-term forks.”
Furthermore, in keeping with him, decreased participation of nodes and validators within the verification course of might jeopardize the decentralization of the community and the integrity of the blockchain.
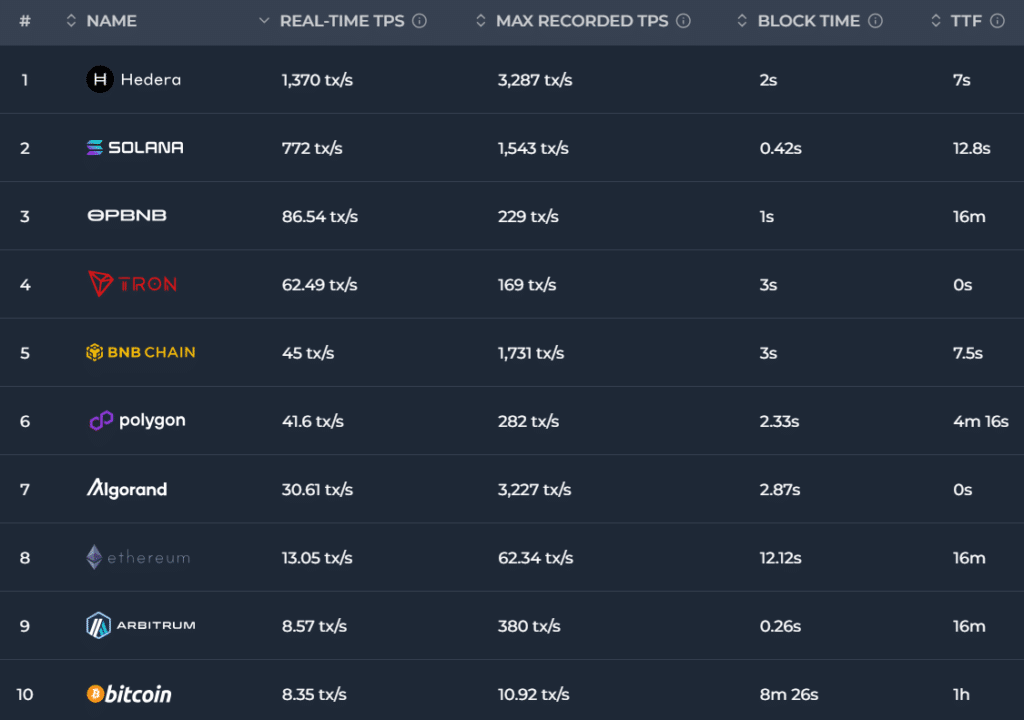
For example, regardless of being decentralized and safe with over one million BTC miners worldwide, the Bitcoin community processes a mean of 8.35 transactions per second (TPS). This determine is considerably decrease than that of centralized cash transmitters akin to Visa, which has a TPS vary of 1,500 to 2,000.
In distinction, Zcash’s blockchain usually operates at a mean velocity of 26 transactions per second (TPS) for unshielded transactions. Nevertheless, a September 2023 report discovered that greater than 50% of Zcash’s hash price was managed by ViaBTC’s mining pool, exposing the community to a 51% danger of assault.
Take Solana (SOL) as one other instance, with a present real-time TPS of 772, in keeping with knowledge from Chainspect. Regardless of the tenth main outage in February 2023, the community has proven excessive stability since then.
In a July 21, 2023 report, the Solana Basis declared 100% uptime for the Solana blockchain. This efficiency adopted enhancements within the ratio of voting to non-voting transactions.
On this case, Luke Nolan, a analysis affiliate at CoinShares, factors out that the principle trade-off was decentralization, and he says “safety has come to a minimal trade-off.”
He emphasizes that the worth to make use of a Solana validator will be fairly excessive, starting from $3,000 to $5,000. These excessive prices make it costly for most of the people to function a Solana validator, which poses the chance of centralization.

In accordance with knowledge from Solana Compass, Solana at present has a complete of two,919 nodes with over 433,000 stakers. The community’s node rely has decreased considerably since March 2023, after reaching an all-time excessive (ATH) of two,564 operational nodes.
Though the variety of Ethereum nodes has repeatedly decreased since mid-January and at present hovers round 7,000, it’s nonetheless 2.4 occasions greater than that of Solana’s working programs.
This quantity is affordable contemplating that Ethereum nodes require decrease {hardware} necessities in comparison with Solana and price between $500 and $1,000. Moreover, the variety of Ethereum stakers can be considerably greater than Solana’s – at present it stands at over 921,000.
Nolan additionally stated that Ethereum has put aside the thought of Layer-1 (L1) scaling in the intervening time to keep away from compromising decentralization or safety. Presently, Ethereum processes a mean of roughly 13 transactions per second (TPS), with the very best recorded TPS being 62.34.
“Generally, I would not say that the variety of validators is the No. 1 measure of decentralization, however from a philosophical perspective you could possibly run an Ethereum node very cheaply and assist the chain transfer ahead even with out staking 32 ETH – though of After all you would not earn something.”
Luke Nolan instructed crypto.information.
Options
To point out that the blockchain trilemma is just not an unbreakable rule, firms are introducing artistic options that problem the concept that velocity and safety are all the time at odds. Let’s discover a few of the finest options that purpose to steadiness scalability, safety and decentralization.
- L2 networks: These options enhance Layer-1 blockchains by rising transaction velocity, decreasing prices, and enhancing total scalability. L2s enable the principle chain to give attention to safety and decentralization, whereas Layer-2 networks present scalability and effectivity. Technically, L2 blockchains inherit the safety of L1 networks.
- Consensus mechanism modifications: New consensus mechanisms, akin to Proof of Stake (PoS) variants, purpose to steadiness safety and velocity with out main compromises. Transferring from Proof of Work (PoW) to PoS will be an essential strategy to improve transaction throughput whereas decreasing processing prices.
- Separated witness (SegWit): Carried out in Bitcoin in 2017, SegWit scales blockchain throughput by separating transaction signatures from transaction knowledge and storing them in another way. This separation improves house effectivity, streamlines authentication, and reduces the general measurement of transaction data.
- Shards: Strategies akin to sharding distribute transaction processing throughout smaller teams of nodes, rising velocity whereas sustaining safety. For instance, Concord blockchain makes use of sharding and at present achieves a finality time of two seconds, whereas Solana’s Time to Finality (TTF) is roughly 12.8 seconds.
- Rollups:
- Zero-knowledge mixtures (zk-rollups): These rollups bundle a whole lot of off-chain transactions and generate a cryptographic proof, additionally known as a zero-knowledge proof.
- Optimistic roll up: These function below the idea that transactions are legitimate by default. They carry out the calculation on the Layer-1 (L1) blockchain solely in case of a dispute. This introduces a remaining delay in verifying the legitimacy of transactions earlier than they attain the L1 community. If a transaction is discovered to be invalid, it may be reversed to keep away from any unfavorable penalties.
Conclusion
Quick blockchains don’t straight sacrifice decentralization and safety; as an alternative, the blockchain trilemma sheds mild on the challenges builders face and the incidental tradeoffs they have to take care of.
“In a nutshell, whereas velocity typically brings challenges versus safety, the blockchain group’s relentless innovation can present some options. It is not nearly selecting between velocity and security; it’s about well designing the blockchain to steadiness each.”
Neville Grech instructed crypto.information.
Dulub emphasizes that “cautious design, rigorous testing, and continued analysis are key to mastering the challenges” related to the blockchain trilemma.

